Design of experiment provides a method by which the treatments are placed at random on the experimental units in such a way that the responses are estimated with the utmost precision possible. Repeat the experiment applying thetreatments to a number of subjects.
Experimental Design Definition And Principles Voxco
Control sources of variation other than the factors being tested by making conditions as similar as possible for all treatment groups.
. The basic principles of experimental designs are randomization replication and local control. B control randomization repetition. Allows us to equalize the effects of unknown or uncontrollable sources of variation.
An experiment is double blind if both the subjects and the researchers measuring responses are unaware of the treatment group for each subject. In this article we will discuss about- 1. Principles of Experimental Designs 3.
Introduction to Design of Experiments. Practical examples and end-of-chapter exercises are the highlights of. These principles make a valid test of significance possible.
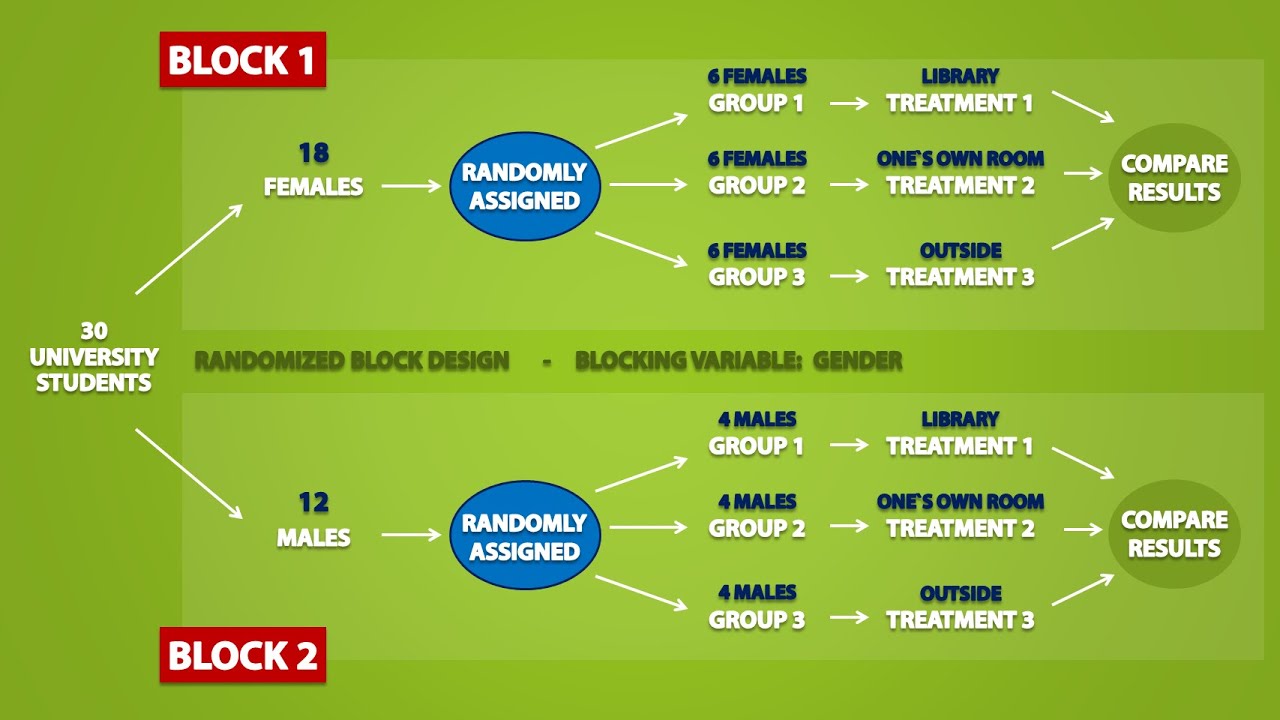
Each of them is described briefly in the following subsections. Experimenters can block. There are three basic principles behind any experimental design.
B control. -Replication of the study repeat the whole thing w different subjects. An experiment is blinded if the subjects do not know which treatment group they are in.
N 1 N 2 c. S 1 S 2 ii. This allows us to equalize the effects of unknown or uncontrollable sources of variation.
The experiment should be reaped more than once. 22 - Sample Size Determination. The random allocation of treatments to the experimental units.
There are three basic principles of design which were developed by Sir Ronald A. To quantify the natural variation between experimental units. This book provides an accessible presentation of concepts from probability theory statistical methods the design of experiments and statistical quality control.
They hire a group of physical trainers and a statistician who recruits healthy adults between the ages of and to participate in a study. A statistical experiment is defined as an ordered procedure which is performed with the objective of verifying determining the. 8 Tests to test all combinations.
YSufficient No XNo Y Necessary Treatment and Control Conditions Control Experimental Blocking Matching Randomization Statistical ANCOVA Multiple Regression Structural Equations Not Identifying the Real Cause. Experimental design Basic principles 1. The repetition of a treatment within an experiment allows.
D randomization control pairing. The 3 Rs Experimental studies. From the field to the data file.
It is full of experiments and research. E comparison blocking pairing. We do this to reduce variation.
Principles of experimental design. Three will be one second order interaction as well in the given design it is between all the three variables ie EV CV1 CV2. What is to be optimized.
C blocking blinding bias avoidance. The basic principles of statistical design of experiments three 1. Randomize to avoid confounding between treatment effects and other unknown effects.
Components of an Experiment Terminology Experimental Design I Terminology Experimental Design II Main Principles of experimental design. Experimental designs are various types of plot arrangements which are used to test a set of treatments to draw valid conclusions about a particular problem. Blinding is meant to protect against experimental artifacts that could.
PART 2 Analysis of. An experiment with insecticides. By doing so the statistical accuracy of.
Ø Single treatment does not produce variations in the results. Randomly assign subjects to treatment groups. Formulate questiongoal in advance 2.
Repeat the entire experiment for differentgroups in different situations. Professor Fisher has enumerated three principles of experimental designs. Principles of experiment design.
Ø They are classically called the Principles of Experimental Design they are. Statistics deals with the study of gathering observing calculating and interpreting the numerical data. 23 - Determining Power.
Meaning of Experimental Designs. There may be attributes of subjects we cant controlthat could affect the outcome of an experiment eggender genetics age etc. Meaning of Experimental Designs 2.
13 - Steps for Planning Conducting and Analyzing an Experiment. Experimental variable with control variable 2 or EV CV 2. The three basic principles of statistical design of experiments are A control comparison confounding.
21 - Simple Comparative Experiments. All possible combinations of the variables are used in the various runs. The first principle of an experimental design is randomization which is a random process of assigning treatments to the experimental units.
-replication within the study by having multiple subjects. The cause must precede the effect in time. Control variable 1 with control variable 2 or CV1 CV2.
STATISTICAL MODEL AND ANALYSIS. Before dealing with experimental designs it. A footwear company wants to test the effectiveness of its new insoles designed to prevent shin splints resulting from running.
Control the effects of lurking variables on the response by ensuring all subjects are affected similarly by these lurking variables. The statistician randomly assigns of the adults. T 1 T 2 b.
Replication Ø The repetition of the treatments under the investigation is called replication. Basic Principles of Experimental Design Cause and Effect. Thus each treatment is applied in many experimental units instead of one.
Experimental variable with control variable 1 or EV CV 1. 113 The Four Principles of Experimental Design 1. Full Factorial Experiment 2 3 1.
11 - A Quick History of the Design of Experiments DOE 12 - The Basic Principles of DOE. Then simply compare two or more treatments. It is shaped by the experience of the two teachers teaching statistical methods and concepts to engineering students over a decade.
The principle of replication.

Basic Principles Of Experimental Design Basic Statistics And Data Analysis

All There Is To Know About Experimental Design Voxco

0 Comments